Reliable Cane Sugar Processing: Making Best Use Of Return and Purity
Reliable Cane Sugar Processing: Making Best Use Of Return and Purity
Blog Article
An Extensive Overview to the Environmental Influence and Sustainability Practices in Cane Sugar Handling
The ecological influence of cane sugar handling presents a complex selection of challenges that warrant cautious exam. From soil destruction and extreme water use to the carbon footprint associated with growing and manufacturing, the repercussions of traditional techniques are significant. What specific practices can be carried out to strike an equilibrium between efficiency and ecological stewardship?
Review of Walking Cane Sugar Processing
Walking stick sugar handling entails a collection of organized actions that change sugarcane into refined sugar. Initially, collected sugarcane is transferred to processing centers, where it undertakes cleaning up to remove dirt and particles. Following this, the walking cane is squashed to draw out juice, which is after that made clear by eliminating impurities through home heating and the enhancement of lime.
The clarified juice undertakes dissipation, where water is eliminated to focus the sugar material. This concentrated syrup is then crystallized with cooling, permitting sugar crystals to form. These crystals are separated from the continuing to be syrup using centrifugation, leading to raw sugar. To attain refined sugar, the raw product undertakes more filtration processes, which might consist of filtering and cleaning to eliminate continuing to be impurities and shade.
The end product is then dried out and packaged for circulation. Throughout this entire procedure, maintaining effectiveness and quality assurance is important to make sure the sugar fulfills market criteria. Each step in walking cane sugar processing not only adds to the final item but likewise has effects for resource use and waste generation, setting the phase for conversations on sustainability and ecological impacts related to sugar manufacturing.
Ecological Challenges of Production
The production of walking stick sugar offers several significant ecological obstacles that warrant attention. One primary issue is the extensive use agrochemicals, consisting of pesticides and fertilizers, which can cause dirt destruction, biodiversity loss, and contamination of local water resources. The drainage from sugarcane areas usually carries these chemicals into nearby environments, disrupting aquatic life and affecting the health and wellness of neighborhoods reliant on these water bodies.
One more obstacle is the high power usage connected with sugarcane processing. The boiling and refining stages require substantial heat, primarily created by melting fossil fuels, adding to greenhouse gas emissions. In addition, the expansive land area needed for sugarcane farming can bring about logging and habitat devastation, further worsening climate adjustment and threatening wild animals.
Furthermore, the labor practices in some areas elevate ethical concerns, as employees might deal with bad working conditions and inadequate earnings. This circumstance frequently bolsters a cycle of hardship in local neighborhoods. Cane Sugar Processing. Dealing with these ecological difficulties is crucial for establishing more lasting practices in walking stick sugar production, eventually profiting both the atmosphere and the areas involved in this sector
Water and Land Use Effect
Water sources and land usage are critical elements in the walking cane sugar industry that dramatically impact the atmosphere. The farming of sugarcane needs significant water input, with estimates suggesting that it can eat up to 2,000 liters of water per kilo of sugar produced. This intensive use water frequently brings about depletion of regional water sources, affecting not only the sugarcane vineyards yet also surrounding ecosystems and communities that count on the very same water sources for agriculture and domestic usage.
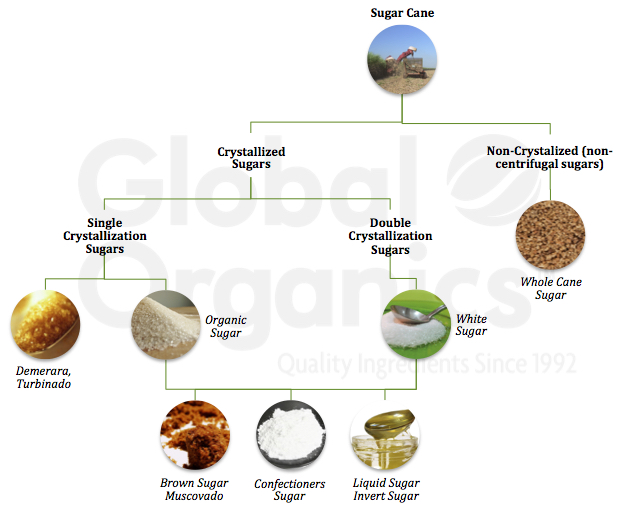
In addition, land use for sugarcane cultivation can result in logging and the conversion of natural habitats right into monoculture plantations. This method lessens biodiversity, interrupts neighborhood environments, and contributes to dirt deterioration. The expansion of sugarcane fields frequently trespasses on important farming land, linked here developing competition for resources in between food and biofuel production.
Sustainable practices, such as maximizing watering methods and carrying out plant turning, are vital to alleviate these effects. By embracing more efficient water use and land monitoring methods, the walking stick sugar industry can reduce its eco-friendly impact, making sure an equilibrium between farming efficiency and environmental conservation.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Greenhouse gas exhausts represent a significant ecological worry within the walking cane sugar handling sector, particularly as farming practices broaden to satisfy international demand. The farming of sugarcane, a plant that prospers in tropical environments, depends heavily on synthetic plant foods and pesticides, which add to laughing gas emissions. Furthermore, land-use modifications, consisting of deforestation click to find out more for brand-new sugarcane vineyards, release carbon dioxide saved in greenery and dirt.
During processing, power intake is an additional significant resource of greenhouse gas exhausts - Cane Sugar Processing. Many sugar mills utilize fossil fuels to power machinery and produce warm, leading to significant carbon impacts. In addition, the transport of raw sugarcane and ended up items includes layers of exhausts with gas combustion in cars
The advancing impact of these discharges worsens climate modification, positioning risks not only to the environment yet additionally to the lasting stability published here of the market. Stakeholders need to acknowledge the urgent need for extensive strategies that address these exhausts. This entails examining present agricultural techniques, refining techniques, and transport systems to recognize areas for improvement and reduction. Resolving greenhouse gas discharges is vital for fostering an extra lasting cane sugar sector in an altering climate.

Sustainable Practices and Innovations
Lasting practices and technologies are progressively vital in the walking stick sugar processing market as stakeholders look for to decrease ecological impacts while keeping productivity. One considerable advancement is the application of incorporated crop monitoring, which optimizes resource usage by combining soil monitoring, pest control, and crop turning strategies. This method improves yield while lessening chemical inputs and protecting dirt health.
Furthermore, the adoption of eco-friendly power sources, such as biomass from sugarcane residues, has gotten grip - Cane Sugar Processing. By transforming waste items right into power, refining facilities can reduce their reliance on fossil fuels, consequently decreasing greenhouse gas exhausts
Water monitoring techniques have actually additionally seen improvements through the recycling and reusing of water in processing plants, substantially minimizing freshwater intake. Technologies in technology, such as precision agriculture, make it possible for farmers to keep an eye on crop health and wellness and source usage extra successfully, guaranteeing lasting growing techniques.
Additionally, certification programs like Fair Profession and Jungle Alliance encourage ecologically responsible farming practices and promote social equity within the supply chain. By embracing these lasting methods and advancements, the walking stick sugar processing sector can boost its durability and contribute favorably to ecological stewardship.
Final Thought
The environmental influence of walking stick sugar processing offers considerable challenges, consisting of soil degradation, high water intake, and greenhouse gas discharges, alongside moral issues connected to labor techniques. Attending to these issues via sustainable techniques, such as integrated plant administration, renewable resource adoption, and water recycling, is crucial. By promoting eco accountable and socially fair approaches in sugar production, the sector can alleviate its unfavorable effects, making sure a more lasting future for both environments and areas entailed in this market.
Cane sugar processing involves a collection of systematic actions that transform sugarcane into polished sugar. Each action in walking stick sugar processing not only adds to the final product however also has ramifications for resource use and waste generation, establishing the stage for conversations on sustainability and ecological impacts connected with sugar manufacturing.
Greenhouse gas emissions stand for a substantial environmental concern within the walking stick sugar processing sector, especially as agricultural techniques expand to fulfill worldwide demand.Sustainable practices and advancements are increasingly essential in the cane sugar processing market as stakeholders look for to reduce ecological impacts while maintaining performance.The ecological effect of walking stick sugar handling offers significant challenges, including soil deterioration, high water usage, and greenhouse gas exhausts, along with moral problems connected to labor techniques.
Report this page